| COVID-19 and the Eye: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature No abstract available |
A Review and Update on Surgical Management of Intraocular Lens Dislocation No abstract available No abstract available |
| Updates in the Management of Corneal Ectasia No abstract available |
| Review: Optimizing DMEK Technique, 2018-2020 No abstract available |
Recent Advances in Pediatric Endothelial Keratoplasty No abstract available No abstract available |
Recent Updates in Femtosecond Laser-assisted Cataract Surgery No abstract available No abstract available |
| Alpha-Gal Syndrome in Ophthalmology and Medicine: Erratum No abstract available |
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(269)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (133)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (136)
-
►
2022
(2046)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (165)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (161)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (165)
-
►
2021
(3028)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (135)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (182)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (324)
-
▼
2020
(1051)
-
▼
Δεκεμβρίου
(292)
-
▼
Δεκ 17
(18)
- Ophthalmology Clinics
- The antiretroviral 2',3'-dideoxycytidine causes mi...
- Cholesterol stimulates the cellular uptake of L-ca...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3820: Circulating IL-13 Is...
- Antibiotics, Vol. 9, Pages 920: A Risk Prediction ...
- Exceptional Regression of Malignant Pleural Mesoth...
- Pembrolizumab-Induced Severe Neuropathy in a Patie...
- Cranial Nerve Metastasis Treated with Radiotherapy...
- Bilateral Encrusted Metallic Stent Successfully Re...
- Successful Treatment of Advanced Thymic Carcinoma ...
- Hepatic Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor Detecte...
- High-Dose Omalizumab versus Ligelizumab for the Tr...
- Celiac Disease and Sensitization to Wheat, Rye, an...
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of Hsa_circ_00025...
- Musashi-1 promotes cancer stem cell properties of ...
- Exosomal miR-126 blocks the development of non-sma...
- MiR-4310 induced by SP1 targets PTEN to promote gl...
- LncRNA ST7-AS1, by regulating miR-181b-5p/KPNA4 ax...
-
▼
Δεκ 17
(18)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (60)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
▼
Δεκεμβρίου
(292)
-
►
2019
(2277)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (18)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (89)
-
►
2018
(26280)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (189)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (6130)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (7050)
-
►
2017
(33948)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (6715)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (6470)
-
►
2016
(4179)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (638)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (526)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (517)
Πέμπτη 17 Δεκεμβρίου 2020
Ophthalmology Clinics
The antiretroviral 2',3'-dideoxycytidine causes mitochondrial dysfunction in proliferating and differentiated HepaRG human cell cultures [Bioenergetics]
|
Cholesterol stimulates the cellular uptake of L-carnitine by the carnitine/organic cation transporter novel 2 (OCTN2) [Bioenergetics]
|
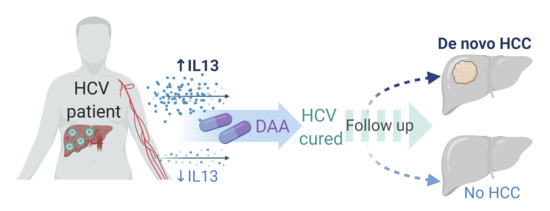
Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3820: Circulating IL-13 Is Associated with De Novo Development of HCC in HCV-Infected Patients Responding to Direct-Acting Antivirals
|
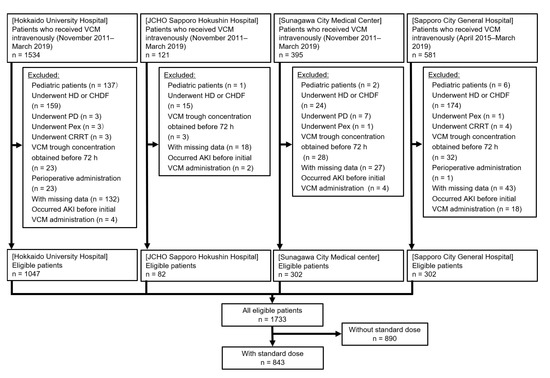
Antibiotics, Vol. 9, Pages 920: A Risk Prediction Flowchart of Vancomycin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury to Use When Starting Vancomycin Administration: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
|
Exceptional Regression of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma with Pembrolizumab Monotherapy
|
Pembrolizumab-Induced Severe Neuropathy in a Patient with Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma after Achieving Complete Response: Guillain-Barré Syndrome-Like Onset
|
Cranial Nerve Metastasis Treated with Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma
|
Bilateral Encrusted Metallic Stent Successfully Removed by Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy Using a Ho:YAG Laser in a Patient with Malignant Myeloma
|
Successful Treatment of Advanced Thymic Carcinoma with Carboplatin plus nab-Paclitaxel and Maintenance Monotherapy with nab-Paclitaxel: Two Case Reports
|
Hepatic Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor Detected in the Fetal Period That Caused an Oncologic Emergency
|
High-Dose Omalizumab versus Ligelizumab for the Treatment of Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: Do Not We Need a Head-To-Head Comparison?
|